Primer:
Domain Name System (DNS) is a service which translates a website name (ipcamtalk.com) to it's static, does not change, internet IP address (172.67.71.1). For you and me it is easier to remember names rather than numbers.
Dynamic Domain Name System (
DDNS) is a service which keeps DNS updated with a device's current address as it's address is
not static but rather can change.
Background:
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) have a pool of Public IP Addresses which they are authorized to use. Large corporations, or individuals, who pay substantial money are able to have specific, assigned static Public IP addresses to their entity. However, most home users (individuals) are provided with a Public IP Address which can be changed at any time by the ISP. For home users the changing IP Address really doesn't matter as they originate the traffic which enters the WWW. There are exceptions to this that the changing IP Address makes difficult; i.e. web hosting, private mail server, etc.
Inbound connections are made to a known name, and the Public IP Address assigned to that name must be updated if/when the IP address changes. To maintain an accurate DNS record to the host which has a changing IP address is the purpose of DDNS.
DDNS for cameras - Commercial/Public IP Address
Cameras have the ability to use DDNS, but it is not always needed/required; typically not needed.
Commercial use of cameras may use DDNS within a company's domain as a simple method to deploy without the need of static or DHCP reservations. Though, the corporation will need to have its own private DDNS server which the cameras use. (they would not connect to a public DDNS server; .ipctddns.com, duckdns.com, no-ip.com, etc)
Also any camera attached to the internet directly with a non-static Public IP Address would use DDNS to allow users a persistent name as a connection definition. Cameras connected to the internet with a Public IP Address could use a public DDNS server to provide an updated device name.
DDNS for cameras - Home Use
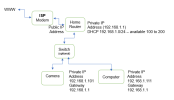
Typically cameras used with the home environment are connected the the home internet through a router. The router enables multiple devices, not just one, to be connected simultaneously. The router is providing DHCP addresses of private IP range to all of the home user's devices. Private IP Addresses are not routable through the internet. Configuring a camera with DDNS having a Private IP Address provides no internet-to-camera accessibility/connectivity.
Home cameras (typically) are set up with static Private IP Addresses within the router's DHCP address space; e.g. 192.168.1.#, 192.168.100.#, etc. Static assignments may be done via DHCP reservations or assigning an IP address directly on the device itself.
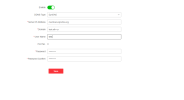
Home use of DDNS is for the device which has a Public IP address. In most cases, this device would be the router. Nearly all modern routers have the ability to be configured with DDNS.
Which are the Private IP Address Ranges?
10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255: This range is used for Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA).