A majority of residential network environments consist of the home's router automatically assigning dynamic IP addresses as the various devices are powered on and request them. Your phone might be assigned an IP of 192.168.1.22, but the following week there is a chance it obtains a different IP (192.168.1.31)... hence the 'dynamic' addressing
Option 1
A device can be manually assigned a static IP address (incls subnet and default gateway) by setting specific information on the device itself. However, this information cannot be randomly chosen, it needs to correlate with information about the existing network. This is why most home networks use the dynamic IP method noted above.
Option 2
Another method for static IP is to program the router reserve specific IP addresses for specific devices. This ensures a single device will always be given the same IP over time. This is achieved by reading a unique number from the respective device (called a MAC address) and pre-associating the MAC address to a specific IP within the router's configuration. You might recall the ISP did this for your cameras at one point. I highly suspect they did this with your old BI server, as well.
Because you've upgraded BI to a new machine you are at the point of trying to determine your old BI servers IP and (hopefully) how it was set... via the router, or via the configuring on the old BI server itself.
How to use ipconfig command
On the old BI server....
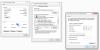
Press Windows key + X then select 'Run'
Type the following in the 'run' box that appears and press 'ok' : cmd
This opens a Command Prompt
Type ipconfig and press enter
This will show you the basic network information from your network adapter(s)
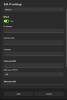
Make note of the values for the following: IP(v4) address, Subnet mask, and default Gateway
You will need to enter this information on your new BI machine via the screenshot you referenced in your last post.