Numerous scientific studies coming out on the effectiveness of masks.
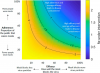
So far, the data looks good that Masks are one aspect of helping to reduce the R value.
Remember the new variations of SARS-CoV-2 are more transmissible, and thus the math is not a simple linear messure.
View attachment 84231
Conclusion
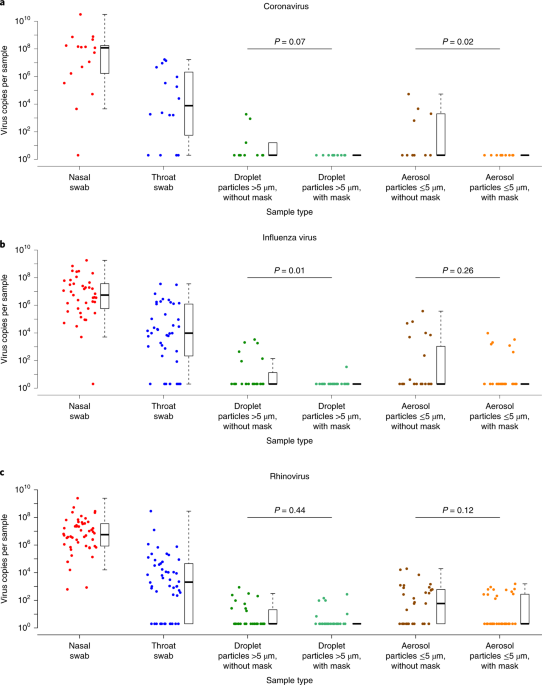
Our review of the literature offers evidence in favor of widespread mask use as source control to reduce community transmission: Nonmedical masks use materials that obstruct particles of the necessary size; people are most infectious in the initial period postinfection, where it is common to have few or no symptoms (
45,
46,
141); nonmedical masks have been effective in reducing transmission of respiratory viruses; and places and time periods where mask usage is required or widespread have shown substantially lower community transmission.
The available evidence suggests that near-universal adoption of nonmedical masks when out in public, in combination with complementary public health measures, could successfully reduce ReRe to below 1, thereby reducing community spread if such measures are sustained. Economic analysis suggests that mask wearing mandates could add 1 trillion dollars to the US GDP (
32,
34).
Models suggest that public mask wearing is most effective at reducing spread of the virus when compliance is high (
39). We recommend that mask use requirements are implemented by governments, or, when governments do not, by organizations that provide public-facing services. Such mandates must be accompanied by measures to ensure access to masks, possibly including distribution and rationing mechanisms so that they do not become discriminatory. Given the value of the source control principle, especially for presymptomatic people, it is not sufficient for only employees to wear masks; customers must wear masks as well.
It is also important for health authorities to provide clear guidelines for the production, use, and sanitization or reuse of face masks, and consider their distribution as shortages allow. Clear and implementable guidelines can help increase compliance, and bring communities closer to the goal of reducing and ultimately stopping the spread of COVID-19.
When used in conjunction with widespread testing, contact tracing, quarantining of anyone that may be infected, hand washing, and physical distancing, face masks are a valuable tool to reduce community transmission. All of these measures, through their effect on ReRe, have the potential to reduce the number of infections. As governments exit lockdowns, keeping transmissions low enough to preserve health care capacity will be critical until a vaccine can be developed.
ref:
The science around the use of masks by the public to impede COVID-19 transmission is advancing rapidly. In this narrative review, we develop an analytical framework to examine mask usage, synthesizing the relevant literature to inform multiple areas: population impact, transmission...

www.pnas.org